Several years ago, cell therapies and cell regeneration medicine were seen as something hard to reach. Currently, stem cell therapy makes possible to treat diseases that conventional medicine faces challenges and limitations.
Cancer, diabetes, alopecia, arthritis, lupus, Alzheimer’s, Sjögren’s syndrome… are just some of the pathologies in which the efficacy of stem cell treatment has been proven. Much of the effectiveness of this treatment depends on the type of transplant, which can be autologous and allogeneic.
In this new post for the ProgenCell blog we will tell you about the characteristics and differences between autologous and allogeneic transplants to help you understand better and answer any questions you might have.
Table of Contents
What are autologous stem cell transplants?
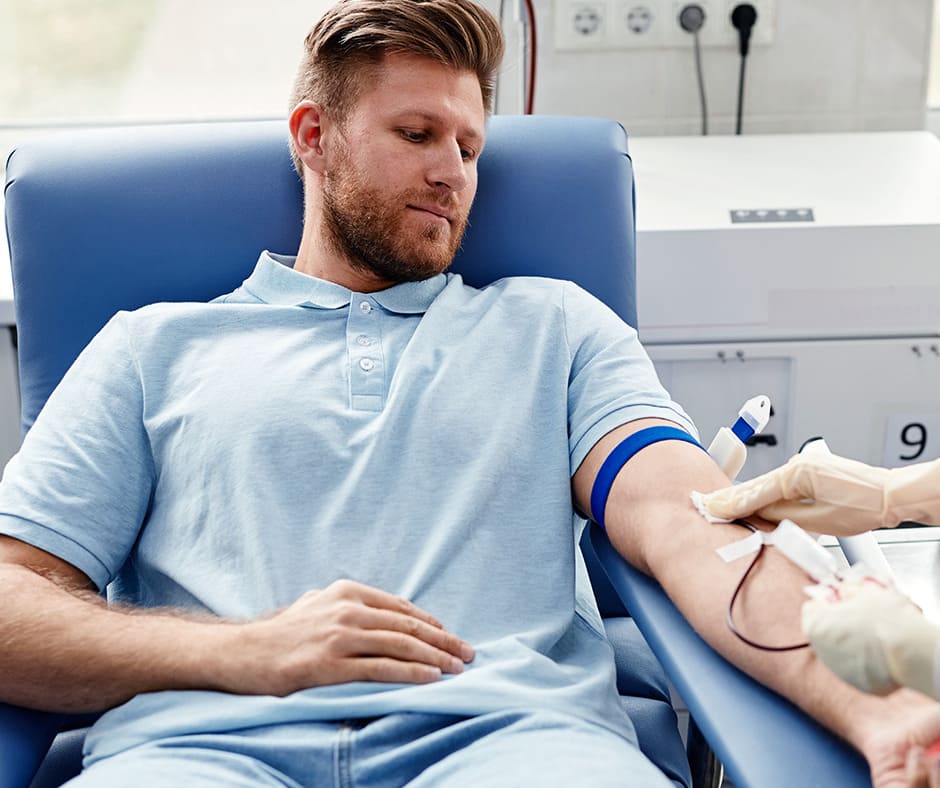
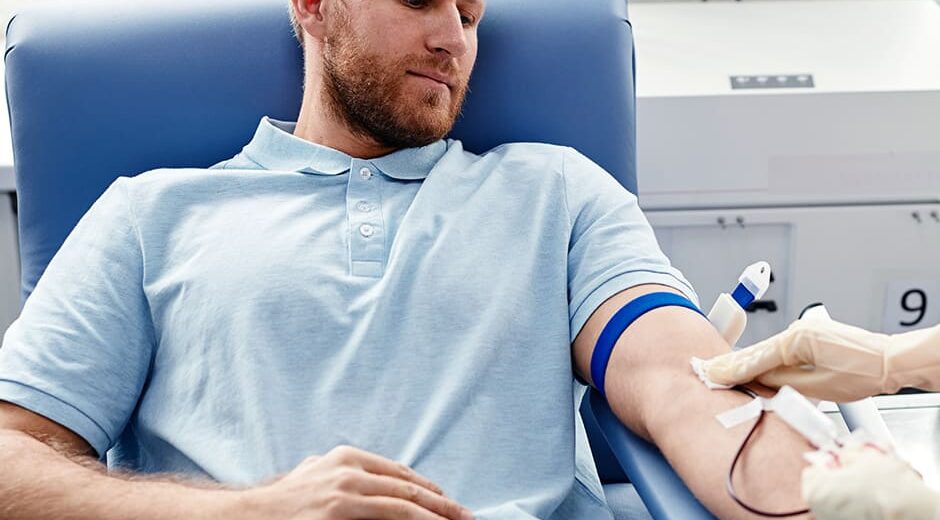
The word autologous means that it comes from the patient’s own body. Therefore, autologous therapy (also called auto transplantation) is performed by the extraction and transfusion of stem cells from the patient. These are obtained from the bone marrow or peripheral blood, extracted, and stored until they are used for transplantation. A process in which the stored stem cells are returned to the patient’s blood.
The use of autologous stem cells significantly reduces the risks of immunological rejection reactions, as well as reactions in which the immune system attacks the transplanted cells and causes inflammatory processes such as dermatitis.
Autologous transplants are used to treat many conditions, especially leukemia, testicular cancer, neuroblastoma, multiple myeloma, among others.
Autologous stem cell treatment process
Autologous stem cell extraction is an outpatient process in which a substance called granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, or GCSF, is injected. That stimulates stem cells to be released from the bone marrow into the bloodstream. Blood tests can determine the number of cells in the bloodstream, and when the number is high, blood is drawn with an intravenous catheter.
Once drawn, the blood goes through an apheresis machine to separate the stem cells and freeze them, or rather cryopreserve them, for several months before the transplant takes place.
However, some clinics use fresh autologous stem cells, meaning, they go through a very short period of cryopreservation to maintain all their characteristics.
Among the many advantages of autologous stem cells is their potential to differentiate into many cell types for tissue regeneration, cells such as neurons, and even organ repair. And best of all, these cells are more likely to persist in the patient’s bloodstream for months or even years and will continue to elicit long-term responses.
On the other hand, in some cases it is not necessary to depress the patient’s body through chemotherapy or radiotherapy, which is undoubtedly a very important advantage.
What are allogeneic stem cell transplants?
The word allogeneic means taken from another individual of the same species. In other words, an allogeneic transplant involves the use of stem cells from another person, called a donor.
In this case, the patient must receive chemotherapy and sometimes radiation therapy to prepare their body to receive the healthy cells from the donor.
While allogeneic transplants carry the risk of infection or rejection by the immune system, this same feature is used as a benefit. That is, stem cells stimulate the immune system to work and destroy malignant cells found in the body. For this reason, allogeneic transplantation is used in different types of cancer.
In general, allogeneic stem cell transplantation is recommended to treat metastatic breast cancer, B-cell, follicular and indolent lymphomas, neoplastic lesions, among other pathologies. Allogeneic transplantation is especially used in the treatment of tumors since stem cells help fight cancer cells.
However, to obtain positive results with the allogeneic transplant, a donor with cells that are very compatible with those of the recipient is required. That is, the donor can be a close relative, such as a parent, sibling, or child.
Allogeneic transplants are considered more attractive because the stem cells come from healthy donors, however the challenge of immune rejection must be considered to prevent a possible loss of benefit and effectiveness.
What is the best option for me?
The reality is that both allogeneic and autologous stem cell transplantation have their advantages and potential drawbacks. This mainly depends on the patient´s health and whether immunosuppression is necessary. However, the recommendation is that you put yourself in the hands of specialists in regenerative medicine to receive the best treatment for your condition.
ProgenCell clinic is certified and authorized by COFEPRIS for stem cell treatment. We have doctors with specialties in regenerative medicine, cell therapy, among others to provide you with the best quality care you deserve.
Browse our website to discover all the services we have for you, such as stem cell therapy for MS, stem cell therapy for knees, stem cells for COPD, for diabetes, stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s and more. If you want to schedule your appointment with a stem cell specialist, or answer a question, contact us by WhatsApp. We’ll gladly assist you!









Facebook Comments